mirror of
https://github.com/pomerium/pomerium.git
synced 2025-07-12 14:28:33 +02:00
proxy: Add user dashboard. [GH-123] proxy/authenticate: Add manual refresh of their session. [GH-73] authorize: Add administrator (super user) account support. [GH-110] internal/policy: Allow administrators to impersonate other users. [GH-110]
400 lines
16 KiB
Markdown
400 lines
16 KiB
Markdown
---
|
|
sidebar: auto
|
|
---
|
|
|
|
# Configuration
|
|
|
|
Pomerium can use a combination of a YAML/JSON/TOML configuration file and [environmental variables] to set configuration settings.
|
|
|
|
If you are coming from a kubernetes or docker background this should feel familiar. If not, check out the following primers.
|
|
|
|
- [Store config in the environment](https://12factor.net/config)
|
|
- [Kubernetes: Environment variables](https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/inject-data-application/define-environment-variable-container/)
|
|
- [Kubernetes: Config Maps](https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/configure-pod-container/configure-pod-configmap/)
|
|
- [Docker: Environment variables](https://docs.docker.com/compose/environment-variables/)
|
|
|
|
In general, any setting specified by environment variable can also be present in the optional config file as the same name but lower cased. Environment variables take precedence.
|
|
|
|
## Global settings
|
|
|
|
These are configuration variables shared by all services, in all service modes.
|
|
|
|
### Service Mode
|
|
|
|
- Environmental Variable: `SERVICES`
|
|
- Config File Key: `services`
|
|
- Type: `string`
|
|
- Default: `all`
|
|
- Options: `all` `authenticate` `authorize` or `proxy`
|
|
|
|
Service mode sets the pomerium service(s) to run. If testing, you may want to set to `all` and run pomerium in "all-in-one mode." In production, you'll likely want to spin up several instances of each service mode for high availability.
|
|
|
|
### Address
|
|
|
|
- Environmental Variable: `ADDRESS`
|
|
- Config File Key: `address`
|
|
- Type: `string`
|
|
- Example: `:https`, `:443`, `:8443`
|
|
- Default: `:https`
|
|
- Required
|
|
|
|
Address specifies the host and port to serve HTTPS and gRPC requests from. If empty, `:https`/`:443` is used.
|
|
|
|
### Administrators
|
|
|
|
- Environmental Variable: `ADMINISTRATORS`
|
|
- Config File Key: `administrators`
|
|
- Type: slice of `string`
|
|
- Example: `"admin@example.com,admin2@example.com"`
|
|
|
|
Administrative users are [super user](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Superuser) that can sign in as another user or group. User impersonation allows administrators to temporarily sign in as a different user.
|
|
|
|
### Shared Secret
|
|
|
|
- Environmental Variable: `SHARED_SECRET`
|
|
- Config File Key: `shared_secret`
|
|
- Type: [base64 encoded] `string`
|
|
- Required
|
|
|
|
Shared Secret is the base64 encoded 256-bit key used to mutually authenticate requests between services. It's critical that secret keys are random, and store safely. Use a key management system or `/dev/urandom/` to generate a key. For example:
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
head -c32 /dev/urandom | base64
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
### Debug
|
|
|
|
- Environmental Variable: `POMERIUM_DEBUG`
|
|
- Config File Key: `pomerium_debug`
|
|
- Type: `bool`
|
|
- Default: `false`
|
|
|
|
By default, JSON encoded logs are produced. Debug enables colored, human-readable logs to be streamed to [standard out](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Standard_streams#Standard_output_(stdout)). In production, it's recommended to be set to `false`.
|
|
|
|
For example, if `true`
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
10:37AM INF cmd/pomerium version=v0.0.1-dirty+ede4124
|
|
10:37AM INF proxy: new route from=httpbin.corp.beyondperimeter.com to=https://httpbin.org
|
|
10:37AM INF proxy: new route from=ssl.corp.beyondperimeter.com to=http://neverssl.com
|
|
10:37AM INF proxy/authenticator: grpc connection OverrideCertificateName= addr=auth.corp.beyondperimeter.com:443
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
If `false`
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
{"level":"info","version":"v0.0.1-dirty+ede4124","time":"2019-02-18T10:41:03-08:00","message":"cmd/pomerium"}
|
|
{"level":"info","from":"httpbin.corp.beyondperimeter.com","to":"https://httpbin.org","time":"2019-02-18T10:41:03-08:00","message":"proxy: new route"}
|
|
{"level":"info","from":"ssl.corp.beyondperimeter.com","to":"http://neverssl.com","time":"2019-02-18T10:41:03-08:00","message":"proxy: new route"}
|
|
{"level":"info","OverrideCertificateName":"","addr":"auth.corp.beyondperimeter.com:443","time":"2019-02-18T10:41:03-08:00","message":"proxy/authenticator: grpc connection"}
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
### Log Level
|
|
|
|
- Environmental Variable: `LOG_LEVEL`
|
|
- Config File Key: `log_level`
|
|
- Type: `string`
|
|
- Options: `debug` `info` `warn` `error`
|
|
- Default: `debug`
|
|
|
|
Log level sets the global logging level for pomerium. Only logs of the desired level and above will be logged.
|
|
|
|
### Certificate
|
|
|
|
- Environmental Variable: either `CERTIFICATE` or `CERTIFICATE_FILE`
|
|
- Config File Key: `certificate` or `certificate_file`
|
|
- Type: [base64 encoded] `string` or relative file location
|
|
- Required
|
|
|
|
Certificate is the x509 _public-key_ used to establish secure HTTP and gRPC connections. If unset, pomerium will attempt to find and use `./cert.pem`.
|
|
|
|
### Certificate Key
|
|
|
|
- Environmental Variable: either `CERTIFICATE_KEY` or `CERTIFICATE_KEY_FILE`
|
|
- Config File Key: `certificate_key` or `certificate_key_file`
|
|
- Type: [base64 encoded] `string`
|
|
- Required
|
|
|
|
Certificate key is the x509 _private-key_ used to establish secure HTTP and gRPC connections. If unset, pomerium will attempt to find and use `./privkey.pem`.
|
|
|
|
### Global Timeouts
|
|
|
|
- Environmental Variables: `TIMEOUT_READ` `TIMEOUT_WRITE` `TIMEOUT_READ_HEADER` `TIMEOUT_IDLE`
|
|
- Config File Key: `timeout_read` `timeout_write` `timeout_read_header` `timeout_idle`
|
|
- Type: [Go Duration](https://golang.org/pkg/time/#Duration.String) `string`
|
|
- Example: `TIMEOUT_READ=30s`
|
|
- Defaults: `TIMEOUT_READ_HEADER=10s` `TIMEOUT_READ=30s` `TIMEOUT_WRITE=0` `TIMEOUT_IDLE=5m`
|
|
|
|
Timeouts set the global server timeouts. For route-specific timeouts, see [policy](./#policy).
|
|
|
|
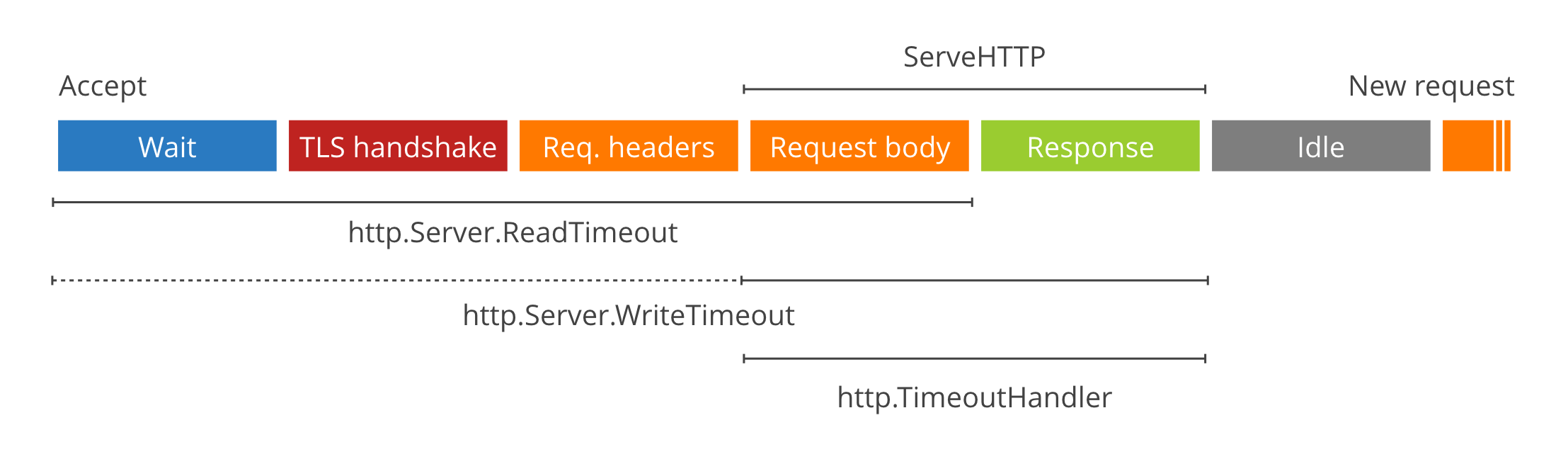
|
|
|
|
> For a deep dive on timeout values see [these](https://blog.cloudflare.com/the-complete-guide-to-golang-net-http-timeouts/) [two](https://blog.cloudflare.com/exposing-go-on-the-internet/) excellent blog posts.
|
|
|
|
### HTTP Redirect Address
|
|
|
|
- Environmental Variable: `HTTP_REDIRECT_ADDR`
|
|
- Config File Key: `http_redirect_addr`
|
|
- Type: `string`
|
|
- Example: `:80`, `:http`, `:8080`
|
|
- Optional
|
|
|
|
If set, the HTTP Redirect Address specifies the host and port to redirect http to https traffic on. If unset, no redirect server is started.
|
|
|
|
### Policy
|
|
|
|
- Environmental Variable: `POLICY`
|
|
- Config File Key: `policy`
|
|
- Type: [base64 encoded] `string` or inline policy structure in config file
|
|
- Required
|
|
|
|
Policy contains route specific settings, and access control details. If you are configuring via POLICY environment variable, just the contents of the policy needs to be passed. If you are configuring via file, the policy should be present under the policy key. For example,
|
|
|
|
<<< @/config-policy-only.yaml
|
|
|
|
A list of policy configuration variables follows.
|
|
|
|
#### From
|
|
|
|
- `yaml`/`json` setting: `from`
|
|
- Type: `string` domain
|
|
- Required
|
|
- Example: `httpbin.corp.example.com`
|
|
|
|
`From` is externally accessible source of the proxied request.
|
|
|
|
#### To
|
|
|
|
- `yaml`/`json` setting: `to`
|
|
- Type: `string` domain
|
|
- Required
|
|
- Example: `httpbin` , `192.1.20.12:20`, `http://neverssl.com`
|
|
|
|
`To` is the destination of a proxied request. It can be an internal resource, or an external resource.
|
|
|
|
#### Allowed Users
|
|
|
|
- `yaml`/`json` setting: `allowed_users`
|
|
- Type: collection of `strings`
|
|
- Required
|
|
- Example: `alice@pomerium.io` , `bob@contractor.co`
|
|
|
|
Allowed users is a collection of whitelisted users to authorize for a given route.
|
|
|
|
#### Allowed Groups
|
|
|
|
- `yaml`/`json` setting: `allowed_groups`
|
|
- Type: collection of `strings`
|
|
- Required
|
|
- Example: `admins` , `support@company.com`
|
|
|
|
Allowed groups is a collection of whitelisted groups to authorize for a given route.
|
|
|
|
#### Allowed Domains
|
|
|
|
- `yaml`/`json` setting: `allowed_domains`
|
|
- Type: collection of `strings`
|
|
- Required
|
|
- Example: `pomerium.io` , `gmail.com`
|
|
|
|
Allowed domains is a collection of whitelisted domains to authorize for a given route.
|
|
|
|
#### CORS Preflight
|
|
|
|
- `yaml`/`json` setting: `cors_allow_preflight`
|
|
- Type: `bool`
|
|
- Optional
|
|
- Default: `false`
|
|
|
|
Allow unauthenticated HTTP OPTIONS requests as [per the CORS spec](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/CORS#Preflighted_requests).
|
|
|
|
#### Public Access
|
|
|
|
- `yaml`/`json` setting: `allow_public_unauthenticated_access`
|
|
- Type: `bool`
|
|
- Optional
|
|
- Default: `false`
|
|
|
|
**Use with caution:** Allow all requests for a given route, bypassing authentication and authorization. Suitable for publicly exposed web services.
|
|
|
|
If this setting is enabled, no whitelists (e.g. Allowed Users) should be provided in this route.
|
|
|
|
#### Route Timeout
|
|
|
|
- `yaml`/`json` setting: `timeout`
|
|
- Type: [Go Duration](https://golang.org/pkg/time/#Duration.String) `string`
|
|
- Optional
|
|
- Default: `30s`
|
|
|
|
Policy timeout establishes the per-route timeout value. Cannot exceed global timeout values.
|
|
|
|
## Authenticate Service
|
|
|
|
### Authenticate Service URL
|
|
|
|
- Environmental Variable: `AUTHENTICATE_SERVICE_URL`
|
|
- Config File Key: `authenticate_service_url`
|
|
- Type: `URL`
|
|
- Required
|
|
- Example: `https://authenticate.corp.example.com`
|
|
|
|
Authenticate Service URL is the externally accessible URL for the authenticate service.
|
|
|
|
### Identity Provider Name
|
|
|
|
- Environmental Variable: `IDP_PROVIDER`
|
|
- Config File Key: `idp_provider`
|
|
- Type: `string`
|
|
- Required
|
|
- Options: `azure` `google` `okta` `gitlab` `onelogin` or `oidc`
|
|
|
|
Provider is the short-hand name of a built-in OpenID Connect (oidc) identity provider to be used for authentication. To use a generic provider,set to `oidc`.
|
|
|
|
See [identity provider] for details.
|
|
|
|
### Identity Provider Client ID
|
|
|
|
- Environmental Variable: `IDP_CLIENT_ID`
|
|
- Config File Key: `idp_client_id`
|
|
- Type: `string`
|
|
- Required
|
|
|
|
Client ID is the OAuth 2.0 Client Identifier retrieved from your identity provider. See your identity provider's documentation, and our [identity provider] docs for details.
|
|
|
|
### Identity Provider Client Secret
|
|
|
|
- Environmental Variable: `IDP_CLIENT_SECRET`
|
|
- Config File Key: `idp_client_secret`
|
|
- Type: `string`
|
|
- Required
|
|
|
|
Client Secret is the OAuth 2.0 Secret Identifier retrieved from your identity provider. See your identity provider's documentation, and our [identity provider] docs for details.
|
|
|
|
### Identity Provider URL
|
|
|
|
- Environmental Variable: `IDP_PROVIDER_URL`
|
|
- Config File Key: `idp_provider_url`
|
|
- Type: `string`
|
|
- Required, depending on provider
|
|
|
|
Provider URL is the base path to an identity provider's [OpenID connect discovery document](https://openid.net/specs/openid-connect-discovery-1_0.html). For example, google's URL would be `https://accounts.google.com` for [their discover document](https://accounts.google.com/.well-known/openid-configuration).
|
|
|
|
### Identity Provider Scopes
|
|
|
|
- Environmental Variable: `IDP_SCOPES`
|
|
- Config File Key: `idp_scopes`
|
|
- Type: `[]string` comma separated list of oauth scopes.
|
|
- Default: `oidc`,`profile`, `email`, `offline_access` (typically)
|
|
- Optional for built-in identity providers.
|
|
|
|
Identity provider scopes correspond to access privilege scopes as defined in Section 3.3 of OAuth 2.0 RFC6749\. The scopes associated with Access Tokens determine what resources will be available when they are used to access OAuth 2.0 protected endpoints. If you are using a built-in provider, you probably don't want to set customized scopes.
|
|
|
|
### Identity Provider Service Account
|
|
|
|
- Environmental Variable: `IDP_SERVICE_ACCOUNT`
|
|
- Config File Key: `idp_service_account`
|
|
- Type: `string`
|
|
- Required, depending on provider
|
|
|
|
Identity Provider Service Account is field used to configure any additional user account or access-token that may be required for querying additional user information during authentication. For a concrete example, Google an additional service account and to make a follow-up request to query a user's group membership. For more information, refer to the [identity provider] docs to see if your provider requires this setting.
|
|
|
|
## Proxy Service
|
|
|
|
### Signing Key
|
|
|
|
- Environmental Variable: `SIGNING_KEY`
|
|
- Config File Key: `signing_key`
|
|
- Type: [base64 encoded] `string`
|
|
- Optional
|
|
|
|
Signing key is the base64 encoded key used to sign outbound requests. For more information see the [signed headers](./signed-headers.md) docs.
|
|
|
|
### Authenticate Service URL
|
|
|
|
- Environmental Variable: `AUTHENTICATE_SERVICE_URL`
|
|
- Config File Key: `authenticate_service_url`
|
|
- Type: `URL`
|
|
- Required
|
|
- Example: `https://authenticate.corp.example.com`
|
|
|
|
Authenticate Service URL is the externally accessible URL for the authenticate service.
|
|
|
|
### Authenticate Internal Service URL
|
|
|
|
- Environmental Variable: `AUTHENTICATE_INTERNAL_URL`
|
|
- Config File Key: `authenticate_internal_url`
|
|
- Type: `string`
|
|
- Optional
|
|
- Example: `pomerium-authenticate-service.pomerium.svc.cluster.local`
|
|
|
|
Authenticate Internal Service URL is the internally routed dns name of the authenticate service. This setting is typically used with load balancers that do not gRPC, thus allowing you to specify an internally accessible name.
|
|
|
|
### Authorize Service URL
|
|
|
|
- Environmental Variable: `AUTHORIZE_SERVICE_URL`
|
|
- Config File Key: `authorize_service_url`
|
|
- Type: `URL`
|
|
- Required
|
|
- Example: `https://access.corp.example.com` or `pomerium-authorize-service.pomerium.svc.cluster.local`
|
|
|
|
Authorize Service URL is the location of the internally accessible authorize service. NOTE: Unlike authenticate, authorize has no publicly accessible http handlers so this setting is purely for gRPC communication.
|
|
|
|
If your load balancer does not support gRPC pass-through you'll need to set this value to an internally routable location (`pomerium-authorize-service.pomerium.svc.cluster.local`) instead of an externally routable one (`https://access.corp.example.com`).
|
|
|
|
### Override Certificate Name
|
|
|
|
- Environmental Variable: `OVERRIDE_CERTIFICATE_NAME`
|
|
- Config File Key: `override_certificate_name`
|
|
- Type: `int`
|
|
- Optional (but typically required if Authenticate Internal Service Address is set)
|
|
- Example: `*.corp.example.com` if wild card or `authenticate.corp.example.com`/`authorize.corp.example.com`
|
|
|
|
When Authenticate Internal Service Address is set, secure service communication can fail because the external certificate name will not match the internally routed service url. This setting allows you to override that check.
|
|
|
|
### Certificate Authority
|
|
|
|
- Environmental Variable: `CERTIFICATE_AUTHORITY` or `CERTIFICATE_AUTHORITY_FILE`
|
|
- Config File Key: `certificate_authority` or `certificate_authority_file`
|
|
- Type: [base64 encoded] `string` or relative file location
|
|
- Optional
|
|
|
|
Certificate Authority is set when behind-the-ingress service communication uses self-signed certificates. Be sure to include the intermediary certificate.
|
|
|
|
### Headers
|
|
|
|
- Environmental Variable: `HEADERS`
|
|
- Config File Key: `headers`
|
|
- Type: map of `strings` key value pairs
|
|
- Example: `X-Content-Type-Options:nosniff,X-Frame-Options:SAMEORIGIN`
|
|
- To disable: `disable:true`
|
|
- Default :
|
|
|
|
```javascript
|
|
X-Content-Type-Options : nosniff,
|
|
X-Frame-Options:SAMEORIGIN,
|
|
X-XSS-Protection:1; mode=block,
|
|
Strict-Transport-Security:max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains; preload,
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
Headers specifies a mapping of [HTTP Header](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/Headers) to be added to proxied requests. _Nota bene_ Downstream application headers will be overwritten by Pomerium's headers on conflict.
|
|
|
|
By default, conservative [secure HTTP headers](https://www.owasp.org/index.php/OWASP_Secure_Headers_Project) are set.
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
### Refresh Cooldown
|
|
|
|
- Environmental Variable: `REFRESH_COOLDOWN`
|
|
- Config File Key: `refresh_cooldown`
|
|
- Type: [Duration](https://golang.org/pkg/time/#Duration) `string`
|
|
- Example: `10m`, `1h45m`
|
|
- Default: `5m`
|
|
|
|
Refresh cooldown is the minimum amount of time between allowed manually refreshed sessions.
|
|
|
|
[base64 encoded]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Base64
|
|
[environmental variables]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Environment_variable
|
|
[identity provider]: ./identity-providers.md
|
|
[letsencrypt]: https://letsencrypt.org/
|
|
[oidc rfc]: https://openid.net/specs/openid-connect-core-1_0.html#AuthRequest
|
|
[script]: https://github.com/pomerium/pomerium/blob/master/scripts/generate_wildcard_cert.sh
|