* authorize: authorization module adds support for per-route access policy. In this release we support the most common forms of identity based access policy: `allowed_users`, `allowed_groups`, and `allowed_domains`. In future versions, the authorization module will also support context and device based authorization policy and decisions. See website documentation for more details. * docs: updated `env.example` to include a `POLICY` setting example. * docs: added `IDP_SERVICE_ACCOUNT` to `env.example` . * docs: removed `PROXY_ROOT_DOMAIN` settings which has been replaced by `POLICY`. * all: removed `ALLOWED_DOMAINS` settings which has been replaced by `POLICY`. Authorization is now handled by the authorization service and is defined in the policy configuration files. * proxy: `ROUTES` settings which has been replaced by `POLICY`. * internal/log: `http.Server` and `httputil.NewSingleHostReverseProxy` now uses pomerium's logging package instead of the standard library's built in one. Closes #54 Closes #41 Closes #61 Closes #58
3.3 KiB
Kubernetes
This quickstart will show you how to deploy Pomerium with Kubernetes. For the purpose of this guide, we will be using Google's Kubernetes Engine. However, there are countless ways to work with Kubernetes:
- Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE)
- Azure Kubernetes Service
- Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (Amazon EKS)
- OpenShift Kubernetes
- Or locally, with minikube
Most of the following steps should be very similar using any other provider.
:::tip
Google Cloud Platform has a free trial with $300 credits.
:::
Prerequisites
- A Google Cloud Account
- A configured identity provider
- Install kubectl
- Install the Google Cloud SDK
Download
Retrieve the latest copy of pomerium's source-code by cloning the repository.
git clone https://github.com/pomerium/pomerium.git $HOME/pomerium
Configure
Edit the the example kubernetes files to match your identity provider settings:
./docs/docs/examples/authorize.deploy.yml./docs/docs/examples/authorize.service.yml./docs/docs/examples/authenticate.deploy.yml./docs/docs/examples/authenticate.service.yml./docs/docs/examples/proxy.deploy.yml./docs/docs/examples/proxy.service.yml./docs/docs/examples/ingress.yml
Place your domain's wild-card TLS certificate (privkey.pem and cert.pem) in the root of the repository. If you don't have one handy, the included script generates one from LetsEncrypt.
Edit ./scripts/kubernetes_gke.sh making sure to change the identity provider secret value to match your identity provider settings.
Run
Run ./scripts/kubernetes_gke.sh which will:
- Provision a new cluster
- Create authenticate, authorize, and proxy deployments.
- Provision and apply authenticate, authorize, and proxy services.
- Configure an ingress load balancer.
sh ./scripts/kubernetes_gke.sh
You should see roughly the following in your terminal. Note, provisioning does take a few minutes.
And if you check out Google's Kubernetes Engine dashboard you'll see something like:
Navigate
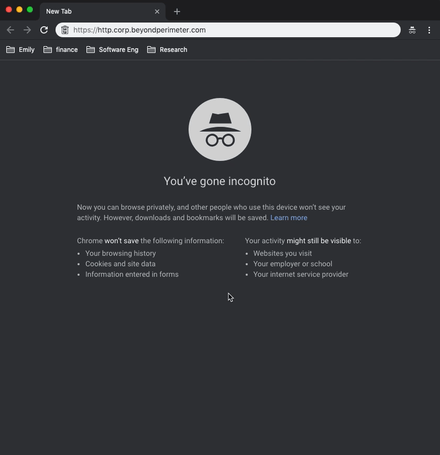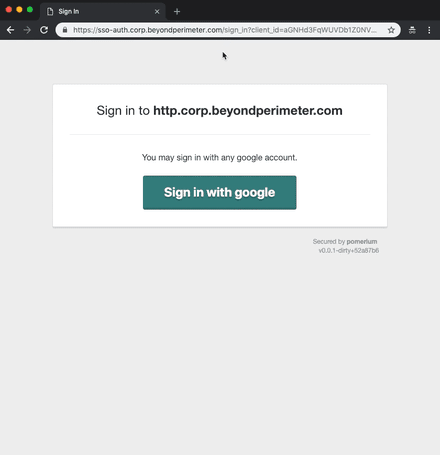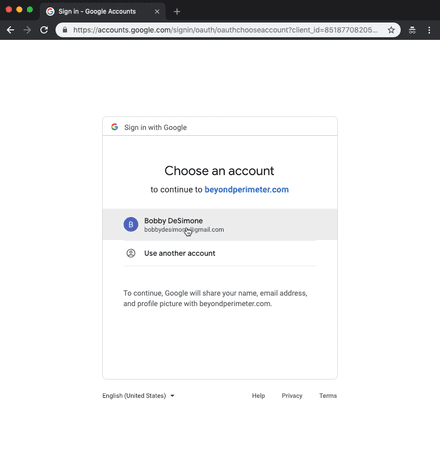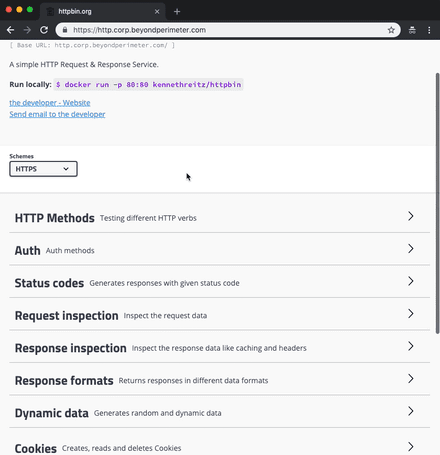
Open a browser and navigate to httpbin.your.domain.com.
You should see something like the following in your browser.