mirror of
https://github.com/badaix/snapcast.git
synced 2025-08-03 16:48:52 +02:00
Merge branch 'develop' into resample
This commit is contained in:
commit
fbaad305d2
13 changed files with 239 additions and 56 deletions
44
README.md
44
README.md
|
|
@ -3,15 +3,15 @@ Snapcast
|
|||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**S**y**n**chronous **a**udio **p**layer
|
||||
|
||||
**S**y**n**chronous **a**udio **p**layer
|
||||
|
||||
[](https://travis-ci.org/badaix/snapcast)
|
||||
[](https://github.com/badaix/snapcast/releases)
|
||||
[](https://www.paypal.me/badaix)
|
||||
|
||||
Snapcast is a multi-room client-server audio player, where all clients are time synchronized with the server to play perfectly synced audio. It's not a standalone player, but an extension that turns your existing audio player into a Sonos-like multi-room solution.
|
||||
The server's audio input is a named pipe `/tmp/snapfifo`. All data that is fed into this file will be send to the connected clients. One of the most generic ways to use Snapcast is in conjunction with the music player daemon ([MPD](http://www.musicpd.org/)) or [Mopidy](https://www.mopidy.com/), which can be configured to use a named pipe as audio output.
|
||||
The server's audio input is a named pipe `/tmp/snapfifo`. All data that is fed into this file will be sent to the connected clients. One of the most generic ways to use Snapcast is in conjunction with the music player daemon ([MPD](http://www.musicpd.org/)) or [Mopidy](https://www.mopidy.com/), which can be configured to use a named pipe as audio output.
|
||||
|
||||
How does it work
|
||||
----------------
|
||||
|
|
@ -22,7 +22,7 @@ The Snapserver reads PCM chunks from the pipe `/tmp/snapfifo`. The chunk is enco
|
|||
* **Opus** lossy low-latency compression
|
||||
|
||||
The encoded chunk is sent via a TCP connection to the Snapclients.
|
||||
Each client does continuos time synchronization with the server, so that the client is always aware of the local server time.
|
||||
Each client does continuous time synchronization with the server, so that the client is always aware of the local server time.
|
||||
Every received chunk is first decoded and added to the client's chunk-buffer. Knowing the server's time, the chunk is played out using ALSA at the appropriate time. Time deviations are corrected by
|
||||
* skipping parts or whole chunks
|
||||
* playing silence
|
||||
|
|
@ -30,9 +30,11 @@ Every received chunk is first decoded and added to the client's chunk-buffer. Kn
|
|||
|
||||
Typically the deviation is smaller than 1ms.
|
||||
|
||||
For more information on the binary protocol, please see the [documentation](doc/binary_protocol.md).
|
||||
|
||||
Installation
|
||||
------------
|
||||
You can either build and install snapcast from source, or on debian systems install a prebuild .deb package
|
||||
You can either build and install snapcast from source, or on Debian systems install a prebuilt .deb package
|
||||
|
||||
### Installation from source
|
||||
Please follow this [guide](doc/build.md) to build Snapcast for
|
||||
|
|
@ -42,10 +44,10 @@ Please follow this [guide](doc/build.md) to build Snapcast for
|
|||
* [Android](doc/build.md#android-cross-compile)
|
||||
* [OpenWrt](doc/build.md#openwrtlede-cross-compile)
|
||||
* [Buildroot](doc/build.md#buildroot-cross-compile)
|
||||
* [Raspberry Pi](doc/build.md#raspberry-pi-cross-compile)
|
||||
* [Raspberry Pi](doc/build.md#raspberry-pi-cross-compile)
|
||||
|
||||
### Install linux packages
|
||||
For Debian download the package for your CPU architecture from the [latest release page](https://github.com/badaix/snapcast/releases/latest), e.g. for Raspberry pi `snapclient_0.x.x_armhf.deb`
|
||||
### Install Linux packages
|
||||
For Debian download the package for your CPU architecture from the [latest release page](https://github.com/badaix/snapcast/releases/latest), e.g. for Raspberry Pi `snapclient_0.x.x_armhf.deb`
|
||||
Install the package:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo dpkg -i snapclient_0.x.x_armhf.deb
|
||||
|
|
@ -82,7 +84,7 @@ On Archlinux, snapcast is available through the AUR. To install, use your favor
|
|||
|
||||
SnapOS
|
||||
------
|
||||
For the brave of you, there is a guide with buildfiles available to build [SnapOS](https://github.com/badaix/snapos), a small and fast-booting OS to run Snapcast, comming in two flavors: [Buildroot](https://github.com/badaix/snapos/blob/master/buildroot-external/README.md) based, or [OpenWrt](https://github.com/badaix/snapos/tree/master/openwrt) based. Please note that there are no pre-build firmware packages available.
|
||||
For the brave of you, there is a guide with buildfiles available to build [SnapOS](https://github.com/badaix/snapos), a small and fast-booting OS to run Snapcast, coming in two flavors: [Buildroot](https://github.com/badaix/snapos/blob/master/buildroot-external/README.md) based, or [OpenWrt](https://github.com/badaix/snapos/tree/master/openwrt) based. Please note that there are no pre-built firmware packages available.
|
||||
|
||||
Configuration
|
||||
-------------
|
||||
|
|
@ -98,9 +100,9 @@ stream = file:///home/user/Musik/Some%20wave%20file.wav?name=File
|
|||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The pipe stream (`stream = pipe`) will per default create the pipe. Sometimes your audio source might insist in creating the pipe itself. So the pipe creation mode can by changed to "not create, but only read mode", using the `mode` option set to `create` or `read`:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
stream = pipe:///tmp/snapfifo?name=Radio&mode=read"
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Test
|
||||
----
|
||||
You can test your installation by copying random data into the server's fifo file
|
||||
|
|
@ -108,19 +110,19 @@ You can test your installation by copying random data into the server's fifo fil
|
|||
$ sudo cat /dev/urandom > /tmp/snapfifo
|
||||
|
||||
All connected clients should play random noise now. You might raise the client's volume with "alsamixer".
|
||||
It's also possible to let the server play a wave file. Simply configure a `file` stream in `/etc/snapserver.conf`, and restart the server:
|
||||
It's also possible to let the server play a WAV file. Simply configure a `file` stream in `/etc/snapserver.conf`, and restart the server:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
[stream]
|
||||
stream = file:///home/user/Musik/Some%20wave%20file.wav?name=test
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
When you are using a Raspberry pi, you might have to change your audio output to the 3.5mm jack:
|
||||
When you are using a Raspberry Pi, you might have to change your audio output to the 3.5mm jack:
|
||||
|
||||
#The last number is the audio output with 1 being the 3.5 jack, 2 being HDMI and 0 being auto.
|
||||
$ amixer cset numid=3 1
|
||||
|
||||
To setup WiFi on a raspberry pi, you can follow this guide:
|
||||
To setup WiFi on a Raspberry Pi, you can follow this guide:
|
||||
https://www.raspberrypi.org/documentation/configuration/wireless/wireless-cli.md
|
||||
|
||||
Control
|
||||
|
|
@ -137,18 +139,18 @@ There is an Android client [snapdroid](https://github.com/badaix/snapdroid) avai
|
|||
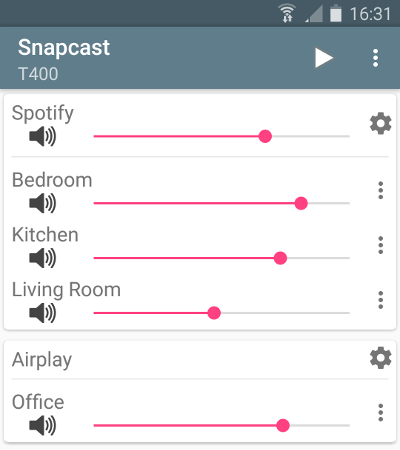
|
||||
|
||||
There is also an unofficial WebApp from @atoomic [atoomic/snapcast-volume-ui](https://github.com/atoomic/snapcast-volume-ui).
|
||||
This app list all clients connected to a server and allow to control individualy the volume of each client.
|
||||
This app lists all clients connected to a server and allows you to control individually the volume of each client.
|
||||
Once installed, you can use any mobile device, laptop, desktop, or browser.
|
||||
|
||||
There is also an [unofficial FHEM module](https://forum.fhem.de/index.php/topic,62389.0.html) from @unimatrix27 which integrates a snapcast controller in to the [FHEM](https://fhem.de/fhem.html) home automation system.
|
||||
There is also an [unofficial FHEM module](https://forum.fhem.de/index.php/topic,62389.0.html) from @unimatrix27 which integrates a snapcast controller into the [FHEM](https://fhem.de/fhem.html) home automation system.
|
||||
|
||||
There is a [snapcast component for Home Assistant](https://home-assistant.io/components/media_player.snapcast/) which integrates a snapcast controller in to the [Home Assistant](https://home-assistant.io/) home automation system.
|
||||
|
||||
For a webinterface in python, see [snapcastr](https://github.com/xkonni/snapcastr), based on [python-snapcast](https://github.com/happyleavesaoc/python-snapcast). This interface controls client volume and assigns streams to groups.
|
||||
For a web interface in Python, see [snapcastr](https://github.com/xkonni/snapcastr), based on [python-snapcast](https://github.com/happyleavesaoc/python-snapcast). This interface controls client volume and assigns streams to groups.
|
||||
|
||||
Another webinterface running on any device, see [snapcast-websockets-ui](https://github.com/derglaus/snapcast-websockets-ui), running entirely in the browser, needs [websockify](https://github.com/novnc/websockify). No configuration needed, features almost all functions, still needs some tuning for the optics.
|
||||
Another web interface running on any device is [snapcast-websockets-ui](https://github.com/derglaus/snapcast-websockets-ui), running entirely in the browser, which needs [websockify](https://github.com/novnc/websockify). No configuration needed; features almost all functions; still needs some tuning for the optics.
|
||||
|
||||
A webinterface called [HydraPlay](https://github.com/mariolukas/HydraPlay) which integrates Snapcast and multiple Mopidy instances. It is JavaScript based and uses Angular 7. A Snapcast websocket proxy server is needed to connect Snapcast to HydraPlay over web sockets.
|
||||
A web interface called [HydraPlay](https://github.com/mariolukas/HydraPlay) integrates Snapcast and multiple Mopidy instances. It is JavaScript based and uses Angular 7. A Snapcast web socket proxy server is needed to connect Snapcast to HydraPlay over web sockets.
|
||||
|
||||
Setup of audio players/server
|
||||
-----------------------------
|
||||
|
|
@ -175,7 +177,7 @@ This [guide](doc/player_setup.md) shows how to configure different players/audio
|
|||
Roadmap
|
||||
-------
|
||||
Unordered list of features that should make it into the v1.0
|
||||
- [X] **Remote control** JSON-RPC API to change client latency, volume, zone, ...
|
||||
- [X] **Remote control** JSON-RPC API to change client latency, volume, zone,...
|
||||
- [X] **Android client** JSON-RPC client and Snapclient
|
||||
- [X] **Streams** Support multiple streams
|
||||
- [X] **Debian packages** prebuild deb packages
|
||||
|
|
@ -185,4 +187,4 @@ Unordered list of features that should make it into the v1.0
|
|||
- [X] **Groups** support multiple Groups of clients ("Zones")
|
||||
- [ ] **JSON-RPC** Possibility to add, remove, rename streams
|
||||
- [ ] **Protocol specification** Snapcast binary streaming protocol, JSON-RPC protocol
|
||||
- [ ] **Ports** Snapclient for Windows, ~~Mac OS X~~, ...
|
||||
- [ ] **Ports** Snapclient for Windows, ~~Mac OS X~~,...
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -106,9 +106,11 @@ ifeq ($(ARCH), x86)
|
|||
else ifeq ($(ARCH), mips)
|
||||
$(eval CXXFLAGS:=$(CXXFLAGS) -DIS_BIG_ENDIAN)
|
||||
$(eval PROGRAM_PREFIX:=$(NDK_DIR)/bin/mipsel-linux-android-)
|
||||
else
|
||||
else ifeq ($(ARCH), arm)
|
||||
$(eval CXXFLAGS:=$(CXXFLAGS) -march=armv7)
|
||||
$(eval PROGRAM_PREFIX:=$(NDK_DIR)/bin/arm-linux-androideabi-)
|
||||
else ifeq ($(ARCH), arm64)
|
||||
$(eval PROGRAM_PREFIX:=$(NDK_DIR)/bin/aarch64-linux-android-)
|
||||
endif
|
||||
endif
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,23 +1,29 @@
|
|||
#/bin/sh
|
||||
|
||||
if [ -z "$NDK_DIR_ARM" ] && [ -z "$NDK_DIR_X86" ]; then
|
||||
echo "Specify at least one NDK_DIR_[ARM|X86]"
|
||||
if [ -z "$NDK_DIR_ARM" ] && [ -z "$NDK_DIR_ARM64" ] && [ -z "$NDK_DIR_X86" ]; then
|
||||
echo "Specify at least one NDK_DIR_[ARM|ARM64|X86]"
|
||||
exit
|
||||
fi
|
||||
|
||||
if [ -z "$ASSETS_DIR" ]; then
|
||||
echo "Specify the snapdroid assets root dir ASSETS_DIR"
|
||||
if [ -z "$JNI_LIBS_DIR" ]; then
|
||||
echo "Specify the snapdroid jniLibs dir JNI_LIBS_DIR"
|
||||
exit
|
||||
fi
|
||||
|
||||
if [ -n "$NDK_DIR_ARM" ]; then
|
||||
export NDK_DIR="$NDK_DIR_ARM"
|
||||
export ARCH=arm
|
||||
make clean; make TARGET=ANDROID -j 4; $NDK_DIR/bin/arm-linux-androideabi-strip ./snapclient; mv ./snapclient "$ASSETS_DIR/bin/armeabi/"
|
||||
make clean; make TARGET=ANDROID -j 4; $NDK_DIR/bin/arm-linux-androideabi-strip ./snapclient; mv ./snapclient "$JNI_LIBS_DIR/armeabi/libsnapclient.so"
|
||||
fi
|
||||
|
||||
if [ -n "$NDK_DIR_ARM64" ]; then
|
||||
export NDK_DIR="$NDK_DIR_ARM64"
|
||||
export ARCH=arm64
|
||||
make clean; make TARGET=ANDROID -j 4; $NDK_DIR/bin/aarch64-linux-android-strip ./snapclient; mv ./snapclient "$JNI_LIBS_DIR/arm64-v8a/libsnapclient.so"
|
||||
fi
|
||||
|
||||
if [ -n "$NDK_DIR_X86" ]; then
|
||||
export NDK_DIR="$NDK_DIR_X86"
|
||||
export ARCH=x86
|
||||
make clean; make TARGET=ANDROID -j 4; $NDK_DIR/bin/i686-linux-android-strip ./snapclient; mv ./snapclient "$ASSETS_DIR/bin/x86/"
|
||||
make clean; make TARGET=ANDROID -j 4; $NDK_DIR/bin/i686-linux-android-strip ./snapclient; mv ./snapclient "$JNI_LIBS_DIR/x86/libsnapclient.so"
|
||||
fi
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,7 +1,8 @@
|
|||
#/bin/sh
|
||||
|
||||
export NDK_DIR_ARM="$1-arm"
|
||||
export NDK_DIR_ARM64="$1-arm64"
|
||||
export NDK_DIR_X86="$1-x86"
|
||||
export ASSETS_DIR="$2"
|
||||
export JNI_LIBS_DIR="$2"
|
||||
|
||||
./build_android.sh
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -58,8 +58,8 @@ FlacDecoder::FlacDecoder() : Decoder(), lastError_(nullptr)
|
|||
FlacDecoder::~FlacDecoder()
|
||||
{
|
||||
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(mutex_);
|
||||
FLAC__stream_decoder_delete(decoder);
|
||||
delete flacChunk;
|
||||
delete decoder;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -222,7 +222,33 @@ cs::time_point_clk Stream::getNextPlayerChunk(void* outputBuffer, const cs::usec
|
|||
return tp;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/*
|
||||
2020-01-12 20-25-26 [Info] Chunk: 7 7 11 15 179 120
|
||||
2020-01-12 20-25-27 [Info] Chunk: 6 6 8 15 212 122
|
||||
2020-01-12 20-25-28 [Info] Chunk: 6 6 7 12 245 123
|
||||
2020-01-12 20-25-29 [Info] Chunk: 5 6 6 9 279 117
|
||||
2020-01-12 20-25-30 [Info] Chunk: 4 5 6 8 312 117
|
||||
2020-01-12 20-25-30 [Error] Controller::onException: read_some: End of file
|
||||
2020-01-12 20-25-30 [Error] Exception in Controller::worker(): read_some: End of file
|
||||
2020-01-12 20-25-31 [Error] Exception in Controller::worker(): connect: Connection refused
|
||||
2020-01-12 20-25-31 [Error] Error in socket shutdown: Transport endpoint is not connected
|
||||
2020-01-12 20-25-32 [Error] Exception in Controller::worker(): connect: Connection refused
|
||||
2020-01-12 20-25-32 [Error] Error in socket shutdown: Transport endpoint is not connected
|
||||
^C2020-01-12 20-25-32 [Info] Received signal 2: Interrupt
|
||||
2020-01-12 20-25-32 [Info] Stopping controller
|
||||
2020-01-12 20-25-32 [Error] Error in socket shutdown: Bad file descriptor
|
||||
2020-01-12 20-25-32 [Error] Exception: Invalid argument
|
||||
2020-01-12 20-25-32 [Notice] daemon terminated.
|
||||
|
||||
=================================================================
|
||||
==22383==ERROR: LeakSanitizer: detected memory leaks
|
||||
|
||||
Direct leak of 5756 byte(s) in 1 object(s) allocated from:
|
||||
#0 0x7f3d60635602 in malloc (/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libasan.so.2+0x98602)
|
||||
#1 0x448fc2 in Stream::getNextPlayerChunk(void*, std::chrono::duration<long, std::ratio<1l, 1000000l> > const&, unsigned long, long) /home/johannes/Develop/snapcast/client/stream.cpp:163
|
||||
|
||||
SUMMARY: AddressSanitizer: 5756 byte(s) leaked in 1 allocation(s).
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
void Stream::updateBuffers(int age)
|
||||
{
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
2
debian/snapclient.service
vendored
2
debian/snapclient.service
vendored
|
|
@ -2,7 +2,7 @@
|
|||
Description=Snapcast client
|
||||
Documentation=man:snapclient(1)
|
||||
Wants=avahi-daemon.service
|
||||
After=network.target time-sync.target sound.target avahi-daemon.service
|
||||
After=network-online.target time-sync.target sound.target avahi-daemon.service
|
||||
|
||||
[Service]
|
||||
EnvironmentFile=-/etc/default/snapclient
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
128
doc/binary_protocol.md
Normal file
128
doc/binary_protocol.md
Normal file
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,128 @@
|
|||
# Snapcast binary protocol
|
||||
|
||||
Each message sent with the Snapcast binary protocol is split up into two parts:
|
||||
- A base message that provides general information like time sent/received, type of the message, message size, etc
|
||||
- A typed message that carries the rest of the information
|
||||
|
||||
## Client joining process
|
||||
|
||||
When a client joins a server, the following exchanges happen
|
||||
|
||||
1. Client opens a TCP socket to the server (default port is 1704)
|
||||
1. Client sends a [Hello](#hello) message
|
||||
1. Server sends a [Server Settings](#server-settings) message
|
||||
1. Server sends a [Stream Tags](#stream-tags) message
|
||||
1. Server sends a [Codec Header](#codec-header) message
|
||||
1. Until the server sends this, the client shouldn't play any [Wire Chunk](#wire-chunk) messages
|
||||
1. The server will now send [Wire Chunk](#wire-chunk) messages, which can be fed to the audio decoder.
|
||||
1. When it comes time for the client to disconnect, the socket can just be closed.
|
||||
|
||||
## Messages
|
||||
|
||||
| Typed Message ID | Name | Notes |
|
||||
|------------------|--------------------------------------|---------------------------------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| 0 | [Base](#base) | The beginning of every message containing data about the typed message |
|
||||
| 1 | [Codec Header](#codec-header) | The codec-specific data to put at the start of a stream to allow decoding |
|
||||
| 2 | [Wire Chunk](#wire-chunk) | A part of an audio stream |
|
||||
| 3 | [Server Settings](#server-settings) | Settings set from the server like volume, latency, etc |
|
||||
| 4 | [Time](#time) | Used for synchronizing time with the server |
|
||||
| 5 | [Hello](#hello) | Sent by the client when connecting with the server |
|
||||
| 6 | [Stream Tags](#stream-tags) | Metadata about the stream for use by the client |
|
||||
|
||||
### Base
|
||||
|
||||
| Field | Type | Description |
|
||||
|-----------------------|--------|---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| type | uint16 | Should be one of the typed message IDs |
|
||||
| id | uint16 | Used in requests to identify the message (not always used) |
|
||||
| refersTo | uint16 | Used in responses to identify which request message ID this is responding to |
|
||||
| received.sec | int32 | The second value of the timestamp when this message was received. Filled in by the receiver. |
|
||||
| received.usec | int32 | The microsecond value of the timestamp when this message was received. Filled in by the receiver. |
|
||||
| sent.sec | int32 | The second value of the timestamp when this message was sent. Filled in by the sender. |
|
||||
| sent.usec | int32 | The microsecond value of the timestamp when this message was sent. Filled in by the sender. |
|
||||
| size | uint32 | Total number of bytes of the following typed message |
|
||||
|
||||
### Codec Header
|
||||
|
||||
| Field | Type | Description |
|
||||
|------------|---------|-------------------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| codec_size | unint32 | Length of the codec string (not including a null character) |
|
||||
| codec | char[] | String describing the codec (not null terminated) |
|
||||
| size | uint32 | Size of the following payload |
|
||||
| payload | char[] | Buffer of data containing the codec header |
|
||||
|
||||
### Wire Chunk
|
||||
|
||||
| Field | Type | Description |
|
||||
|----------------|---------|---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| timestamp.sec | int32 | The second value of the timestamp when this part of the stream was recorded |
|
||||
| timestamp.usec | int32 | The microsecond value of the timestamp when this part of the stream was recorded |
|
||||
| size | uint32 | Size of the following payload |
|
||||
| payload | char[] | Buffer of data containing the codec header |
|
||||
|
||||
### Server Settings
|
||||
|
||||
| Field | Type | Description |
|
||||
|---------|--------|----------------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| size | uint32 | Size of the following JSON string |
|
||||
| payload | char[] | JSON string containing the message (not null terminated) |
|
||||
|
||||
Sample JSON payload (whitespace added for readability):
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"bufferMs": 1000,
|
||||
"latency": 0,
|
||||
"muted": false,
|
||||
"volume": 100
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- `volume` can have a value between 0-100 inclusive
|
||||
|
||||
### Time
|
||||
|
||||
| Field | Type | Description |
|
||||
|----------------|---------|------------------------------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| latency.sec | int32 | The second value of the latency between the server and the client |
|
||||
| latency.usec | int32 | The microsecond value of the latency between the server and the client |
|
||||
|
||||
### Hello
|
||||
|
||||
| Field | Type | Description |
|
||||
|---------|--------|----------------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| size | uint32 | Size of the following JSON string |
|
||||
| payload | char[] | JSON string containing the message (not null terminated) |
|
||||
|
||||
Sample JSON payload (whitespace added for readability):
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"Arch": "x86_64",
|
||||
"ClientName": "Snapclient",
|
||||
"HostName": "my_hostname",
|
||||
"ID": "00:11:22:33:44:55",
|
||||
"Instance": 1,
|
||||
"MAC": "00:11:22:33:44:55",
|
||||
"OS": "Arch Linux",
|
||||
"SnapStreamProtocolVersion": 2,
|
||||
"Version": "0.17.1"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Stream Tags
|
||||
|
||||
| Field | Type | Description |
|
||||
|---------|--------|----------------------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| size | uint32 | Size of the following JSON string |
|
||||
| payload | char[] | JSON string containing the message (not null terminated) |
|
||||
|
||||
Sample JSON payload (whitespace added for readability):
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"STREAM": "default"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
[According to the source](https://github.com/badaix/snapcast/blob/master/common/message/stream_tags.hpp#L55-L56), these tags can vary based on the stream.
|
||||
16
doc/build.md
16
doc/build.md
|
|
@ -39,7 +39,7 @@ For Arch derivates:
|
|||
$ sudo pacman -S base-devel
|
||||
$ sudo pacman -S alsa-lib avahi libvorbis opus-dev flac alsa-utils boost
|
||||
|
||||
For Fedora (and probably RHEL, CentOS & Scientific Linux, but untested):
|
||||
For Fedora (and probably RHEL, CentOS, & Scientific Linux, but untested):
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo dnf install @development-tools
|
||||
$ sudo dnf install alsa-lib-devel avahi-devel libvorbis-devel opus-devel flac-devel libstdc++-static
|
||||
|
|
@ -96,7 +96,7 @@ If you don't have boost installed or in your standard include paths, you can cal
|
|||
## FreeBSD (Native)
|
||||
Install the build tools and required libs:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo pkg install gmake gcc bash avahi libogg libvorbis flac
|
||||
$ sudo pkg install gmake gcc bash avahi libogg libvorbis libopus flac
|
||||
|
||||
### Build Snapserver
|
||||
`cd` into the Snapserver src-root directory:
|
||||
|
|
@ -145,7 +145,7 @@ These can be set either in the [global configuration](https://wiki.gentoo.org/wi
|
|||
fi
|
||||
echo 'media-sound/snapcast client server flac
|
||||
|
||||
If for example you only wish to build the server and *not* the client then preceed the server `USE` flag with `-` i.e.
|
||||
If for example you only wish to build the server and *not* the client then precede the server `USE` flag with `-` i.e.
|
||||
|
||||
echo 'media-sound/snapcast client -server
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -213,22 +213,24 @@ http://developer.android.com/ndk/guides/standalone_toolchain.html
|
|||
```
|
||||
$ cd /SOME/LOCAL/PATH/android-ndk-r17/build/tools
|
||||
$ ./make_standalone_toolchain.py --arch arm --api 16 --stl libc++ --install-dir <android-ndk dir>-arm
|
||||
$ ./make_standalone_toolchain.py --arch arm64 --api 21 --stl libc++ --install-dir <android-ndk dir>-arm64
|
||||
$ ./make_standalone_toolchain.py --arch x86 --api 16 --stl libc++ --install-dir <android-ndk dir>-x86
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Build Snapclient
|
||||
Cross compile and install FLAC, ogg, and tremor (only needed once):
|
||||
Cross compile and install FLAC, opus, ogg, and tremor (only needed once):
|
||||
|
||||
$ cd <snapcast dir>/externals
|
||||
$ make NDK_DIR=<android-ndk dir>-arm ARCH=arm
|
||||
$ make NDK_DIR=<android-ndk dir>-arm64 ARCH=aarch64
|
||||
$ make NDK_DIR=<android-ndk dir>-x86 ARCH=x86
|
||||
|
||||
Compile the Snapclient:
|
||||
|
||||
$ cd <snapcast dir>/client
|
||||
$ ./build_android_all.sh <android-ndk dir> <snapdroid assets dir>
|
||||
$ ./build_android_all.sh <android-ndk dir> <snapdroid jniLibs dir>
|
||||
|
||||
The binaries for `armeabi` and `x86` will be copied into the Android's assets directory (`<snapdroid assets dir>/bin/`) and so will be bundled with the Snapcast App.
|
||||
The binaries for `armeabi`, `arm64-v8a` and `x86` will be copied into the Android's jniLibs directory (`<snapdroid jniLibs dir>/`) and so will be bundled with the Snapcast App.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## OpenWrt/LEDE (Cross compile)
|
||||
|
|
@ -288,7 +290,7 @@ Clone Buildroot to some place in your home directory (`<buildroot dir>`):
|
|||
$ BUILDROOT_VERSION=2016.11.2
|
||||
$ git clone --branch $BUILDROOT_VERSION --depth=1 git://git.buildroot.net/buildroot
|
||||
|
||||
The `<snapcast dir>/buildroot` is currently setup as an external Buildroot folder following the [recommended structure](https://buildroot.org/downloads/manual/manual.html#customize-dir-structure). As of [Buildroot 2016.11](https://git.buildroot.net/buildroot/tag/?h=2016.11) you may specify multiple BR2_EXTERNAL trees. If you are using a version of Buildroot prior to this, then you will need to manually merge `<snapcast dir>/buildroot` with your existing Buildroot external tree.
|
||||
The `<snapcast dir>/buildroot` is currently set up as an external Buildroot folder following the [recommended structure](https://buildroot.org/downloads/manual/manual.html#customize-dir-structure). As of [Buildroot 2016.11](https://git.buildroot.net/buildroot/tag/?h=2016.11) you may specify multiple BR2_EXTERNAL trees. If you are using a version of Buildroot prior to this, then you will need to manually merge `<snapcast dir>/buildroot` with your existing Buildroot external tree.
|
||||
|
||||
Now configure buildroot with the [required packages](/buildroot/configs/snapcast_defconfig) (you can also manually add them to your project's existing defconfig):
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -1,15 +1,15 @@
|
|||
Setup of audio players/server
|
||||
-----------------------------
|
||||
Snapcast can be used with a number of different audio players and servers, and so it can be integrated into your favorite audio-player solution and make it synced-multiroom capable.
|
||||
The only requirement is that the player's audio can be redirected into the Snapserver's fifo `/tmp/snapfifo`. In the following configuration hints for [MPD](http://www.musicpd.org/) and [Mopidy](https://www.mopidy.com/) are given, which are base of other audio player solutions, like [Volumio](https://volumio.org/) or [RuneAudio](http://www.runeaudio.com/) (both MPD) or [Pi MusicBox](http://www.pimusicbox.com/) (Mopidy).
|
||||
The only requirement is that the player's audio can be redirected into the Snapserver's fifo `/tmp/snapfifo`. In the following configuration hints for [MPD](http://www.musicpd.org/) and [Mopidy](https://www.mopidy.com/) are given, which are the base of other audio player solutions, like [Volumio](https://volumio.org/) or [RuneAudio](http://www.runeaudio.com/) (both MPD) or [Pi MusicBox](http://www.pimusicbox.com/) (Mopidy).
|
||||
|
||||
The goal is to build the following chain:
|
||||
|
||||
audio player software -> snapfifo -> snapserver -> network -> snapclient -> alsa
|
||||
|
||||
#### Streams
|
||||
Snapserver can read audio from several input streams, which are configured in the `snapserver.conf` file (default location is `/etc/snapserver.conf`), the config file can be changed the `-c` parameter.
|
||||
Within the config file a list of input streams can be configures in the `[stream]` section:
|
||||
Snapserver can read audio from several input streams, which are configured in the `snapserver.conf` file (default location is `/etc/snapserver.conf`); the config file can be changed with the `-c` parameter.
|
||||
Within the config file a list of input streams can be configured in the `[stream]` section:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
[stream]
|
||||
|
|
@ -22,7 +22,7 @@ stream = pipe:///tmp/snapfifo?name=default
|
|||
|
||||
#### About the notation
|
||||
In this document some expressions are in brackets:
|
||||
* `<angle brackets>`: the whole expression must be replaced with you specific setting
|
||||
* `<angle brackets>`: the whole expression must be replaced with your specific setting
|
||||
* `[square brackets]`: the whole expression is optional and can be left out
|
||||
* `[key=value]`: if you leave this option out, `value` will be the default for `key`
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -30,16 +30,17 @@ For example:
|
|||
```
|
||||
stream = spotify:///librespot?name=Spotify[&username=<my username>&password=<my password>][&devicename=Snapcast][&bitrate=320]
|
||||
```
|
||||
* `username` and `password` are both optional in this case. You need to specify none of both of them
|
||||
* `bitrate` is optional. If not configured, 320 will be used. Same for `devicename`
|
||||
* `username` and `password` are both optional in this case. You need to specify neither or both of them.
|
||||
* `bitrate` is optional. If not configured, `320` will be used.
|
||||
* `devicename` is optional. If not configured, `Snapcast` will be used.
|
||||
|
||||
A valid usage would be for instance:
|
||||
For instance, a valid usage would be:
|
||||
```
|
||||
stream = spotify:///librespot?name=Spotify&bitrate=160
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### MPD
|
||||
To connect [MPD](http://www.musicpd.org/) to the Snapserver, edit `/etc/mpd.conf`, so that mpd will feed the audio into the snapserver's named pipe
|
||||
To connect [MPD](http://www.musicpd.org/) to the Snapserver, edit `/etc/mpd.conf`, so that mpd will feed the audio into the snapserver's named pipe.
|
||||
|
||||
Disable alsa audio output by commenting out this section:
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -54,7 +55,7 @@ Disable alsa audio output by commenting out this section:
|
|||
#}
|
||||
|
||||
Add a new audio output of the type "fifo", which will let mpd play audio into the named pipe `/tmp/snapfifo`.
|
||||
Make sure that the "format" setting is the same as the format setting of the Snapserver (default is "48000:16:2", which should make resampling unnecessary in most cases)
|
||||
Make sure that the "format" setting is the same as the format setting of the Snapserver (default is "48000:16:2", which should make resampling unnecessary in most cases).
|
||||
|
||||
audio_output {
|
||||
type "fifo"
|
||||
|
|
@ -76,7 +77,7 @@ To test your mpd installation, you can add a radio station by
|
|||
#output = autoaudiosink
|
||||
output = audioresample ! audioconvert ! audio/x-raw,rate=48000,channels=2,format=S16LE ! wavenc ! filesink location=/tmp/snapfifo
|
||||
|
||||
With newer kernels one might also have to change this sysctl-setting as default settings has changed recently: `sudo sysctl fs.protected_fifos=0`
|
||||
With newer kernels one might also have to change this sysctl-setting, as default settings have changed recently: `sudo sysctl fs.protected_fifos=0`
|
||||
|
||||
See https://unix.stackexchange.com/questions/503111/group-permissions-for-root-not-working-in-tmp for more details. You need to run this after each reboot or add it to /etc/sysctl.conf or /etc/sysctl.d/50-default.conf depending on distribution.
|
||||
|
||||
|
|
@ -128,27 +129,27 @@ pcm.writeFile {
|
|||
### PulseAudio
|
||||
Redirect the PulseAudio stream into the snapfifo:
|
||||
|
||||
audio player software -> PulseAudio -> PulsaAudio pipe sink -> snapfifo -> snapserver -> network -> snapclient -> Alsa
|
||||
audio player software -> PulseAudio -> PulseAudio pipe sink -> snapfifo -> snapserver -> network -> snapclient -> Alsa
|
||||
|
||||
PulseAudio will create the pipe file for itself and will fail if it already exsits, see the [Configuration section](https://github.com/badaix/snapcast#configuration) in the main readme file on how to change the pipe creation mode to read-only.
|
||||
PulseAudio will create the pipe file for itself and will fail if it already exists; see the [Configuration section](https://github.com/badaix/snapcast#configuration) in the main README file on how to change the pipe creation mode to read-only.
|
||||
|
||||
Load the module `pipe-sink` like this:
|
||||
|
||||
pacmd load-module module-pipe-sink file=/tmp/snapfifo sink_name=Snapcast rate=48000
|
||||
pacmd update-sink-proplist Snapcast device.description=Snapcast
|
||||
|
||||
It might be neccessary to set the pulse audio latency environment variable to 60 msec: `PULSE_LATENCY_MSEC=60`
|
||||
It might be neccessary to set the PulseAudio latency environment variable to 60 msec: `PULSE_LATENCY_MSEC=60`
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### AirPlay
|
||||
Snapserver supports [shairport-sync](https://github.com/mikebrady/shairport-sync) with `stdout` backend.
|
||||
Snapserver supports [shairport-sync](https://github.com/mikebrady/shairport-sync) with the `stdout` backend.
|
||||
1. Build shairport-sync with `stdout` backend: `./configure --with-stdout --with-avahi --with-ssl=openssl --with-metadata`
|
||||
2. Copy the `shairport-sync` binary somewhere to your `PATH`, e.g. `/usr/local/bin/`
|
||||
3. Configure snapserver with `stream = airplay:///shairport-sync?name=Airplay[&devicename=Snapcast][&port=5000]`
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Spotify
|
||||
Snapserver supports [librespot](https://github.com/librespot-org/librespot) with `pipe` backend.
|
||||
Snapserver supports [librespot](https://github.com/librespot-org/librespot) with the `pipe` backend.
|
||||
1. Build and copy the `librespot` binary somewhere to your `PATH`, e.g. `/usr/local/bin/`
|
||||
2. Configure snapserver with `stream = spotify:///librespot?name=Spotify[&username=<my username>&password=<my password>][&devicename=Snapcast][&bitrate=320][&onstart=<start command>][&onstop=<stop command>][&volume=<volume in percent>][&cache=<cache dir>]`
|
||||
* Valid bitrates are 96, 160, 320
|
||||
|
|
@ -169,4 +170,4 @@ Audio captured from line-in can be redirected to the snapserver's pipe, e.g. by
|
|||
[cpipe](https://github.com/b-fitzpatrick/cpiped)
|
||||
|
||||
#### PulseAudio
|
||||
`parec >/tmp/snapfifo` (defaults to 44.1kHz,16bit,stereo)
|
||||
`parec >/tmp/snapfifo` (defaults to 44.1kHz, 16bit, stereo)
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
7
externals/Makefile
vendored
7
externals/Makefile
vendored
|
|
@ -32,7 +32,7 @@ ifndef NDK_DIR
|
|||
$(error android NDK_DIR is not set)
|
||||
endif
|
||||
ifndef ARCH
|
||||
$(error ARCH is not set ("arm" or "x86"))
|
||||
$(error ARCH is not set ("arm" or "aarch64" or "x86"))
|
||||
endif
|
||||
ifeq ($(ARCH), x86)
|
||||
$(eval CPPFLAGS:=-DLITTLE_ENDIAN=1234 -DBIG_ENDIAN=4321 -DBYTE_ORDER=LITTLE_ENDIAN)
|
||||
|
|
@ -40,8 +40,11 @@ ifeq ($(ARCH), x86)
|
|||
else ifeq ($(ARCH), arm)
|
||||
$(eval CPPFLAGS:=-U_ARM_ASSEM_)
|
||||
$(eval PROGRAM_PREFIX:=$(NDK_DIR)/bin/arm-linux-androideabi-)
|
||||
else ifeq ($(ARCH), aarch64)
|
||||
$(eval CPPFLAGS:=-U_ARM_ASSEM_ -DLITTLE_ENDIAN=1234 -DBIG_ENDIAN=4321 -DBYTE_ORDER=LITTLE_ENDIAN)
|
||||
$(eval PROGRAM_PREFIX:=$(NDK_DIR)/bin/aarch64-linux-android-)
|
||||
else
|
||||
$(error ARCH must be "arm" or "x86")
|
||||
$(error ARCH must be "arm" or "aarch64" or "x86")
|
||||
endif
|
||||
$(eval CC:=$(PROGRAM_PREFIX)clang)
|
||||
$(eval CXX:=$(PROGRAM_PREFIX)clang++)
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -36,6 +36,16 @@ OggEncoder::OggEncoder(const std::string& codecOptions) : Encoder(codecOptions),
|
|||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
OggEncoder::~OggEncoder()
|
||||
{
|
||||
ogg_stream_clear(&os_);
|
||||
vorbis_block_clear(&vb_);
|
||||
vorbis_dsp_clear(&vd_);
|
||||
vorbis_comment_clear(&vc_);
|
||||
vorbis_info_clear(&vi_);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
std::string OggEncoder::getAvailableOptions() const
|
||||
{
|
||||
return "VBR:[-0.1 - 1.0]";
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
@ -29,6 +29,8 @@ class OggEncoder : public Encoder
|
|||
{
|
||||
public:
|
||||
OggEncoder(const std::string& codecOptions = "");
|
||||
~OggEncoder() override;
|
||||
|
||||
void encode(const msg::PcmChunk* chunk) override;
|
||||
std::string getAvailableOptions() const override;
|
||||
std::string getDefaultOptions() const override;
|
||||
|
|
|
|||
Loading…
Add table
Add a link
Reference in a new issue